
It tracks your skill level as you tackle progressively more difficult questions. In numerical analysis, the condition number is the infinitesimal relative change in the output for a relative change in the input, and is thus a ratio of logarithmic derivatives. IXL's SmartScore is a dynamic measure of progress towards mastery, rather than a percentage grade.In mathematical finance, the Greek λ is the logarithmic derivative of derivative price with respect to underlying price. I have to compute fractional-order derivative and integral of natural logarithmic function, log(t).Exponential growth and exponential decay are processes with constant logarithmic derivative. Answer (1 of 4): Let y2log x Taking log on both sides, log ylog x·log 2 Differentiate both sides with respect to x, 1/y·dy/dx1/x·log 2 (d(log x)/dx1/x.
Is therefore a pullback of the invariant form. There are, however, functions for which logarithmic differentiation is the only method we can use. We could have differentiated the functions in the example and practice problem without logarithmic differentiation. Is invariant under dilation (replacing X by aX for a constant). Practice 5: Use logarithmic differentiation to find the derivative of f(x) (2x+1) 3. First, assign the function to y y y, then take the natural logarithm of. ( log u v ) ′ = ( log u + log v ) ′ = ( log u ) ′ + ( log v ) ′. To derive the function x x xx xx, use the method of logarithmic differentiation. For example, since the logarithm of a product is the sum of the logarithms of the factors, we have Many properties of the real logarithm also apply to the logarithmic derivative, even when the function does not take values in the positive reals. 2 Computing ordinary derivatives using logarithmic derivatives.That's the derivative of y equals 100 minus 3 log x. So my answer simplifies to -3 over ln 10. That's going to be 1 over ln of 10 times 1 over x. I have -3 times the derivative of the log base 10 of x. Can we exploit this fact to determine the derivative of the natural logarithm Here we. The differentiation of log is only under the base e, e, e, but we can differentiate under other bases, too. Now 100, this is just a constant, Its derivative is going to be 0. The natural logarithm ln(y) is the inverse of the exponential function. Derivatives of logarithmic functions are mainly based on the chain rule.However, we can generalize it for any differentiable function with a logarithmic function. This is the derivative of 100, minus 3 times, the derivative of log x.
#Find derivative of log how to
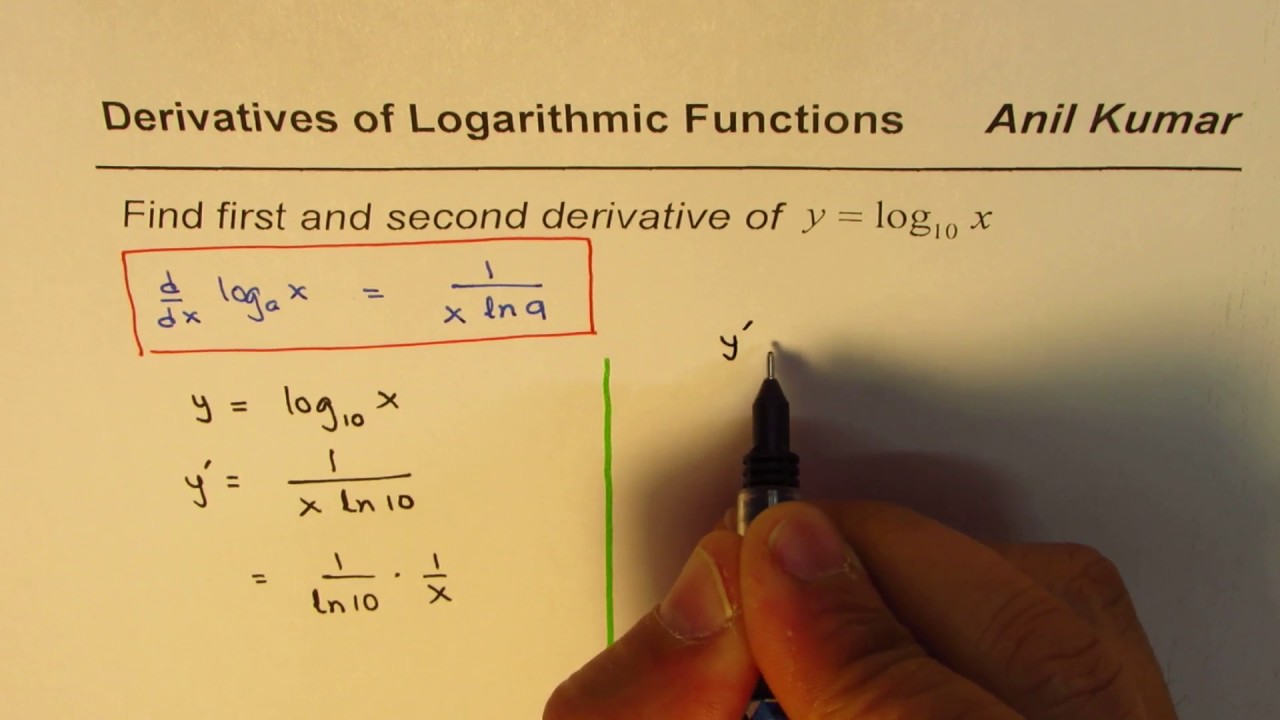
It explains how to find the derivative of natural loga. I can use the sum rule and constant multiple rule. This calculus video tutorial provides a basic introduction into derivatives of logarithmic functions. This is the derivative of 100 minus 3 log x. Remember, when you see log, and the base isn't written, it's assumed to be the common log, so base 10 log. Let's find the derivative of 100 minus 3 log x. So 1 over ln5 times 1 over x.Ī slightly harder example here. Differentiating logarithmic functions using log properties. Practice: Differentiate logarithmic functions. Worked example: Derivative of log (x²+x) using the chain rule. According to this formula, it's 1 over the natural log of the base, 5, times 1 over x. Derivative of logx (for any positive base a1) Practice: Logarithmic functions differentiation intro. If y equals the log base 5 of x, what's the derivative? Dy/dx is the derivative of log base 5 of x. That's the derivative of the log base a of x. That's a constant, so that can be pulled out. Let's observe that this division by lna is just a multiplication by 1 over lna. So if I wanted to differentiate the log of some other base a, I would first change it to this form The derivative with respect to x of lnx over lna. Of course you can change to any other base, but I'm going to change natural log, because I have this formula. To get the derivatives of other logarithms, I'm going to use the change of base formula. First of all, recall that the derivative of natural log is 1 over x. We haven't yet talked about derivatives of other logarithms. So we've talked about the derivative of natural log.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
